Aflutter Ecg. Atrial flutter causes characteristic ecg changes, as discussed below. Atrial flutter is a supraventricular tachycardic arrhythmia that tends to occur in individuals of an advanced age, although it is linked to endurance sports, also. Typical ecg findings include the presence of p waves and qrs complexes that have no association with each other , due to the atria and ventricles functioning independently. Typical atrial flutter is widely known and recognised easily by clinical cardiologists however it does not always present a typical electrocardiographic pattern. Electrocardiography (ecg or ekg) frequently makes the diagnosis by showing saw tooth flutter waves in several (ii, iii. Afib and atypical aflutter requires more expertise and radiofrequency ablation has lower success rate. Differences between ecg wave strip patterns. Atrial flutter is diagnosed by you medical history, history of symptoms, and a physical exam. Sawtooth baseline → flutter waves. During atrial flutter the atria depolarize in an organized circular movement. Atrial flutter is an abnormal heart rhythm that occurs in the atria of the heart. For our 4th lesson, we continue our look at atrial and junctional arrhythmias.we start off talking about one of the most common arrhythmias that you will. How to make the difference between atrial fibrillation (afib) and atrial flutter and in particular between atypical atrial flutter and coarse atrial fibrillation. The ecg criteria to diagnose atrial flutter are discussed including clockwise and counterclockwise, typical vs atypical atrial flutter, and different conduction patterns such as 1:1, 2:1, 3:1, 4:1 and 5:1. Atrial flutter is an abnormal cardiac rhythm caused by rapid atrial activity usually from reentry atrial circuits.
Aflutter Ecg : Qrs Interval • Litfl Medical Blog • Ecg Library Basics
The 12 Rhythms of Christmas: Atrial Flutter | EMS 12 Lead. Atrial flutter is diagnosed by you medical history, history of symptoms, and a physical exam. Atrial flutter is an abnormal heart rhythm that occurs in the atria of the heart. Sawtooth baseline → flutter waves. Atrial flutter causes characteristic ecg changes, as discussed below. Afib and atypical aflutter requires more expertise and radiofrequency ablation has lower success rate. Differences between ecg wave strip patterns. During atrial flutter the atria depolarize in an organized circular movement. Typical atrial flutter is widely known and recognised easily by clinical cardiologists however it does not always present a typical electrocardiographic pattern. Atrial flutter is an abnormal cardiac rhythm caused by rapid atrial activity usually from reentry atrial circuits. Typical ecg findings include the presence of p waves and qrs complexes that have no association with each other , due to the atria and ventricles functioning independently. For our 4th lesson, we continue our look at atrial and junctional arrhythmias.we start off talking about one of the most common arrhythmias that you will. Electrocardiography (ecg or ekg) frequently makes the diagnosis by showing saw tooth flutter waves in several (ii, iii. Atrial flutter is a supraventricular tachycardic arrhythmia that tends to occur in individuals of an advanced age, although it is linked to endurance sports, also. The ecg criteria to diagnose atrial flutter are discussed including clockwise and counterclockwise, typical vs atypical atrial flutter, and different conduction patterns such as 1:1, 2:1, 3:1, 4:1 and 5:1. How to make the difference between atrial fibrillation (afib) and atrial flutter and in particular between atypical atrial flutter and coarse atrial fibrillation.
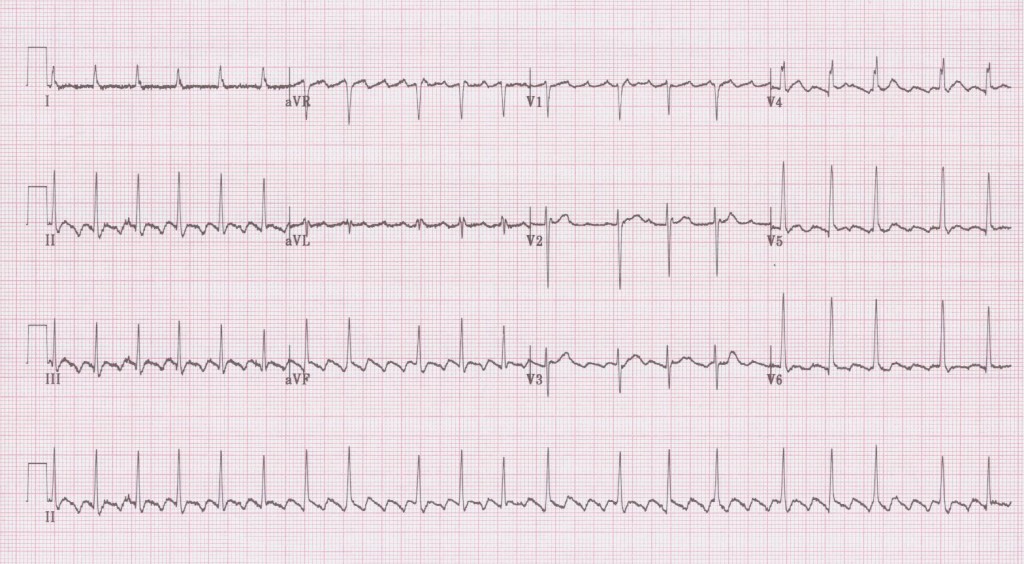
It may be difficult to distinguish atypical aflutter from coarse afib.
Designed for use by medical professionals. Atrial flutter is less common, but has similar symptoms (feeling faint, tiredness, palpitations, shortness of breath or dizziness). It's caused by an abnormal electrical circuit that makes the atria beat quickly and flutter instead of fully squeezing. Webmd provides a comprehensive look at the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of atrial flutter and atrial fibrillation. This quiz uses a simulated patient monitor with moving waveform instead of a paper tracing. About a third of people with atrial flutter also have atrial fibrillation. Atrial flutter is an abnormal cardiac rhythm caused by rapid atrial activity usually from reentry atrial circuits. It may be difficult to distinguish atypical aflutter from coarse afib. Atrial flutter is a regular supraventricular tachycardia characterized by an atrial heart rate between 240/min and 340/min (typically 300/min), atrioventricular (av) node conduction block, and a sawtooth pattern on an electrocardiogram (ecg). Atrial flutter is a rapid regular atrial rhythm due to an atrial macroreentrant circuit. From ecg to clinical management. Afib and atypical aflutter requires more expertise and radiofrequency ablation has lower success rate. Atrial flutter is a supraventricular tachycardic arrhythmia that tends to occur in individuals of an advanced age, although it is linked to endurance sports, also. This lesson talks about the characteristics of atrial flutter, how to identify it on an ekg, the complications, nursing interventions and treatments. Differences between ecg wave strip patterns. It affects the upper heart chambers (atria). 'coarse afib' has an f wave amplitude> 0.5 mm, which can mimic. Atrial flutter is diagnosed by you medical history, history of symptoms, and a physical exam. Atrial flutter is an abnormal heart rhythm that occurs in the atria of the heart. How to make the difference between atrial fibrillation (afib) and atrial flutter and in particular between atypical atrial flutter and coarse atrial fibrillation. Atrial flutter is an abnormality in the beating of the heart, also known as arrhythmias. The ecg criteria to diagnose atrial flutter are discussed including clockwise and counterclockwise, typical vs atypical atrial flutter, and different conduction patterns such as 1:1, 2:1, 3:1, 4:1 and 5:1. Atrial flutter is the second most common pathological tachyarrhythmia. Use our lessons, drills, tutorials and quizzes. Atrial flutter is an abnormal cardiac rhythm characterized by rapid, regular atrial depolarizations at a characteristic rate of approximately 300 beats/min and. Atrial flutter is an abnormality in the beating of the heart. Atrial flutter is one of the more common abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmias). Distinguish atypical aflutter from coarse afib: For our 4th lesson, we continue our look at atrial and junctional arrhythmias.we start off talking about one of the most common arrhythmias that you will. Symptoms include palpitations, shortness of breath, anxiety, and weakness. Typical atrial flutter is widely known and recognised easily by clinical cardiologists however it does not always present a typical electrocardiographic pattern.